
Union classification is the means by the which a company defines which union will represent its employees. Currently, only one union represents the employees of one company[1]/professional category (what we call union unity), but this may change.

The head section of article 464 of the Consolidated Labor Laws (CLT) provides that "the payment of salaries shall be accompanied by a receipt, signed by the employee." The sole paragraph of this legal provision provides that "proof of deposit into a bank account opened for that purpose, on behalf of the employee, with the consent of the latter, in a credit facility near the place of work shall be required." In other words, a bank deposit made by the employer into an account opened for this purpose, with the consent of the employee, is equated to a signed payment receipt.

Law No. 13,467/2017, known as the Labor Reform, has been in force for more than a year, but, to date, not all of the amendments it proposed to the Consolidated Labor Laws (CLT) have been reviewed by the Labor Courts. This is the case for the exceptions to salary equalization, such as organized career frameworks and job and salary plans.

The Labor Reform (Law No. 13,467/17) brought in various changes to labor law, especially from the point of view of collective rights. One of the most significant issues was the interest shown by the legislator in promoting collective autonomy, whereby it established, among other assumptions, prevalence of what is negotiated over what is legislated and a limitation on accrued rights, with the end of the applicability of collective rules after their abrogation, as previously supported by the case law.[1]

Federal Decree No. 9,571/2018 has been drawing the attention of companies by assuming effective legal rules on liability for the chain of production. The decree stipulates the guidelines on human rights to be adopted by Brazilian and multinational companies of all sizes, in the context of their whole operation.

In August of this year, the Federal Supreme Court (STF) ruled that outsourcing is lawful in all stages of the production process, be it ancillary or main activities, in deciding Argument of Breach of a Basic Precept (ADPF) No. 324.

The need to create specific breastfeeding areas for employees of shops is a matter that has not yet been settled among the panels of the Superior Labor Court (TST). In September, over a few weeks, the court handed down judgments in diametrically opposed terms, in two cases whose claims were identical: the creation of space for safekeeping, security, and assistance for shop employees.
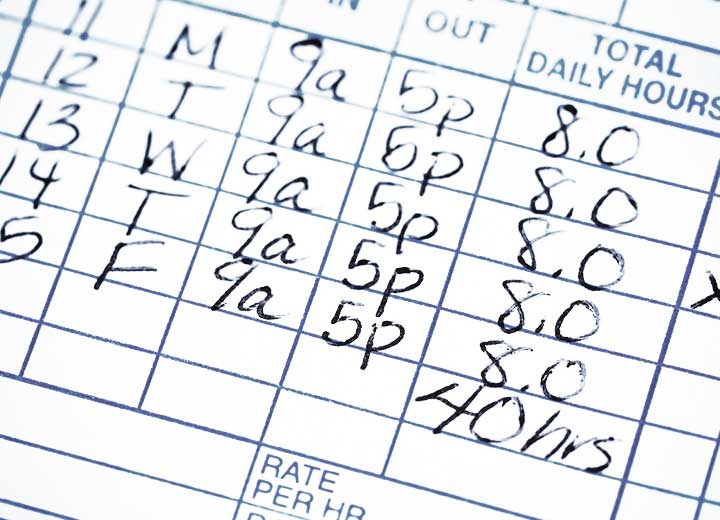
The Superior Labor Court (TST) granted relief to an appeal filed by a company seeking to recognize as valid a collective bargaining agreement that authorized the use of an alternative system for controlling work hours, in which the employee only records overtime and not the other points of the workday. The decision was rendered on October 9 as part of Case No. 0002016-02.2011.5.03.0011.

One of the greatest labor challenges facing the Brazilian business community today is compliance with the minimum quotas for the hiring of apprentices and people with disabilities or rehabilitated workers.

Law No. 13,467/17 (the Labor Reform) inserted article 652, f, into the Consolidated Labor Laws (CLT), thus expanding the jurisdiction of the Labor Courts to decide on the ratification of extrajudicial settlements. However, even with this change, parties (companies and workers) are having difficulty having these settlements ratified at trial level, since the judges allege the supposed unconstitutionality of article 652, f, of the CLT.

Every labor relationship is based on mutual trust between the parties. Every day, new products are created, new production techniques are implemented, and new markets are pursued. Employees have access to information that, if disclosed, may jeopardize the earnings of their companies and their very existence.

Decree No. 9,507/18, published on September 24, extends the possibility of hiring outsourced workers by the direct federal public administration and public companies and companies controlled by the Federal Government.

Ordinance No. 1,287/2017, published in December by the Ministry of Labor, prohibits the granting of a "negative service fee" under the Worker's Food Program (PAT). This fee represents a discount granted by meal and food card operators as a way to become more competitive and attract customers. In practice, the purchasing company acquires a monthly credit to be distributed via cards to its employees, but disburses a smaller amount due to the discount granted.

The Federal Supreme Court (STF) recognized by a majority of votes (7 to 4)[1] the lawfulness of outsourcing companies’ core business activity.

Article 507-A of the Consolidated Labor Laws (CLT), included by the Labor Reform (Law No. 13,467/2017), stipulated that, for employees whose remuneration exceeds twice the ceiling of the General Social Security Regime (RGPS), it will be possible to enter into arbitration agreements, provided that it is per their own initiative or their express agreement, under the terms established in Law No. 9,307/1996 (Arbitration Law).